We are GST!
Introducing our research group
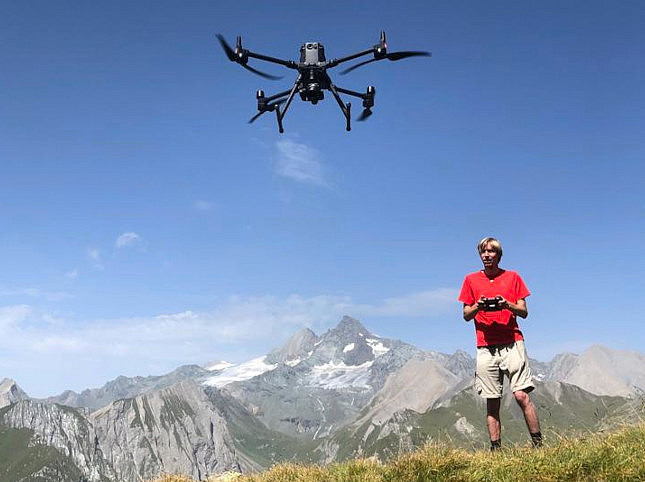

By Geospatial Technologies we mean the combination of geographic technologies (remote sensing, geographic information systems, cartography, spatial-statistical methods, geovisualization and environmental monitoring) at the interface of research, teaching and application. Our overriding goal is the further development of methods for interdisciplinary and integrative research questions. In doing so, we are increasingly pursuing
-
networking in international research projects and cooperations, such as IUFRO, EARSeL, ISAG, Slovak Academy of Science, Yıldız Technical University (Turkey), Tribhuvan University (Nepal), ...
-
the implementation of regional problems and solutions;
-
the development of inter- and transdisciplinary research designs;
-
the sustainable pooling of expertise in the university and regional environment, in particular in the cooperation between NAWI GRAZ and Graz University of Technology, but also with the City of Graz, the Province of Styria, Joanneum Research, Gesäuse National Park and many more;
-
the embedding of research activities in the university's profile-forming areas of "Climate Change Graz" and "Dimensioning Europeanization";
-
the promotion of young scientists.
We develop methods and solutions for cities and regions. Our analyses and visualizations support urban and regional planning, especially with regard to necessary adaptations to climate change.
In the research field of climate change - mountains - vegetation, we are dedicated to monitoring changes in the earth's surface, especially in the mountains. We use time series data from satellites together with data from various other sources (UAV, aerial images, laser scanning, ...).
Another focus is the interaction between geotechnology and humans. We have developed GIS applications specifically for people with disabilities; we use geotechnologies for historical and social issues and investigate the impact of digital technologies on our society. Big data and innovative visualization techniques play a major role in this.
Ongoing and completed Master's theses
| Name | Topic | Subject Description |
| Annika Aichholzer | Wall-to-Wall LiDAR Analysis of Forest Parameters in Slovenia- Methodology and Practical Applications | This thesis investigates, how LiDAR data can help in the identification of (potentially) old-growth forests in Slovenia. |
| Marie Bechtold | Survey of forest vitality from drone data | In this thesis, two different drone systems and cameras are tested in order to be able to observe and document the vitality of trees in a timely and cost-saving manner. |
| Nik Čepirlo | Combining remote sensing and crowdsourcing in support of the EU regulation on deforestation-free products (finished, AGEO award!) | This thesis investigated the use of Sentinel-2 time series data for deforestation detection in the Ivory Coast to support the EU regulation on deforestation-free products with space data. |
| Clemens Freytag | Detecting the Understudied: A Multi-Criteria Approach Integrating Remote Sensing, GIS, and In-Situ Data to Identify Forest Degradation in the Tropics | The aim of this thesis is to improve the detection of forest degradation by integrating time series analysis of Sentinel-2 images using advanced filtering techniques and crowdsourced in-situ observations. In addition, a multi-criteria GIS analysis is conducted to further improve accuracy. The results will help to fulfil the requirements of the EUDR by including so-far often neglected forest degradation. |
| Selina Schaar | Detection of old-growth beech forests using Sentinel-2 time series imagery | Selina used Sentinel-2 data and LiDAR data for the classification of tree species and old-growthiness in Austrian beech forests. |
| Hannah Scheicher | Combination of LiDAR and Sentinel data for wall-to-wall vegetation parameter assessment in the National Park Kalkalpen | This thesis assessed and showed the potential of combining airborne and spaceborne LiDAR data with Sentinel-2 satellite images for mapping different vegetation parameters. |
| Niklas Terler | Geodata and automated GIS processes to increase efficiency in the implementation of fibre optic infrastructure | The aim of this thesis is to optimise the operational handling processes in the implementation of fibre optic infrastructure using geodata and GIS analysis tools. |
| Jasmin Sailer | Opportunities and Challenges of Augmented Reality in Tourism: A Case Study of a Native App for Graz | This master's thesis explores how augmented reality can enrich cultural tourism by designing a mobile app for Graz that overlays geolocated historic postcards and enables visitors to share their experiences through spatially anchored comments, audio, and stories |
| Benjamin Signitzer | Estimating Urban Pedestrian Volume through Multi-Source Free/Open-Data Fusion | This master's thesis introduces an open, flexible, and robust framework to assess pedestrian frequency at the city scale by fusing heterogeneous open data, including OpenStreetMap attributes, meteorological records, public event calendars, population density rasters, and street-level imagery |
| Simon Herz | Colouring Austria: Integrating AI-Derived Roof Typologies into an Open Building-Data Platform | This master's project pioneers the Austrian node of the Colouring Cities platform by creating nationwide, reproducible data workflows that use AI models to enrich building attributes. |
| Karina Löffler | Out of Sight, Out of Mind: A Visibility-Based Classification for Identifying Suitable Agricultural Land for Vertical Agri-Photovoltaic Systems | This master's thesis uses large-scale viewshed analysis to classify agricultural land by the visibility of vertical photovoltaic panels, pinpointing sites where installations would have minimal visual impact and thus greater public acceptance |
| Marco Kirchmair | What is the seasonal pattern of rock glacier dynamics in the Hohe Tauern? A geotechnology-based case study at the Dösen rock glacier, Ankogel group | This master thesis investigates the movement behaviour of the Dösen rock glacier in high spatial and temporal resolution by means of repeated high-precision optical drone images. The aim is to gain new insights into this "essential climate variable" for the assessment of permafrost changes. |
| Fabian Wack | Comparison of 3D measurement methods (terrestrial laser scanning, airborne laser scanning and photogrammetry (drone)) for rock monitoring in the Alps | This master's thesis examines various methods and, above all, their intersection to optimise rock monitoring in the Alpine region. |
If you are interested, please contact the supervisor!
| Supervisor | Subject | Subject description |
| Thibaud Chassin | Stimulating PPGIS with Pre-Filled Map Visualisations | The goal of this project is to create a user study that compares alternative pre-filled map designs to see how each enhances the quantity and quality of public contributions in participatory GIS |
| Thibaud Chassin | Designing 3D Visual Aids for Efficient Interaction with Urban Digital Models | This project focuses on designing and evaluating 3D perceptual cues that guide users' attention and actions, improving speed and accuracy when performing tasks in an interactive urban model |
| Thibaud Chassin | Agent-Based Simulation of Urban Emotional Contagion | This project aims to introduce a spatial-temporal agent-based model to simulate how emotions spread through city populations as people move and interact along everyday pathways |
Our projects
EUDR-Compliant Coffee Cooperatives using Space Technologies in East Africa
Objective CocoCoST is a third-party funded project that systematically integrates dynamically changing input data to maintain current and reliable risk analyses and mapping products for gravitational mass movements.
Project duration: 01.12.2025 – 31.05.2028
Funding: Austrian Research Promotion Agency (FFG)
Funding: € 60.460,--
Staff members: Manuela Hirschmugl (project leader), Florian Lippl
Cooperation partners: University of Life Sciences – BOKU (AT), Beetle ForTech (AT), JOANNEUM RESEARCH GmbH (AT)
Project description
The EU Regulation of Deforestation-free Products (EUDR) requires operators to prove that commodities such as coffee and coca do not originate from recently deforested land or have contributed to forest degradation. Coffee smallholder farmers in East Africa face major challenges in fulfilling these requirements: faulty automated remote sensing deforestation detection systems can result in incorrect exclusion, threatening their livelihoods, and farmers lack technical means for transparent field boundary mapping and proving land use status. These issues were identified during research visits in the predecessor project DeFree, which focused on deforestation detection from Copernicus time series data and crowdsourcing. CoCoCoST builds upon knowledge gained in DeFee, such as the lack of smartphones available to smallholders limited digital literacy. The project develops cost-efficient GNSS positioning devices for cooperatives to map their fields, creates cutting-edge post-processing methods for seamless GIS integration, improves classification accuracy for agroforestry systems by integrating new sensors (P-Band Biomassm NiSAR, ROSE-L) with Copernicus data, and analyzes sustainable funding options that benefit cooperatives directly while serving as business models for involved Austrian small and medium-sized enterprises.
Assessment of Landslide Risk in Dynamic Environments
Objective ALaDyn is a third-party funded project that systematically integrates dynamically changing input data to maintain current and reliable risk analyses and mapping products for gravitational mass movements.
Project duration: 01.01.2025 – 31.12.2026
Funding: Austrian Research Promotion Agency (FFG)
Funding: € 40.417,--
Staff members: Manuela Hirschmugl (project leader), Hanna Bambizava, Christian Bauer, Lisa Bieringer
Cooperation partners: JOANNEUM RESEARCH GmbH (AT), Lugitsch & Partner Ziviltechniker GmbH (AT)
Project description
Risk analyses and maps that serve as a basis for planning decisions regarding gravitational mass movements are increasingly being generated using models. The quality and timeliness of these products depend substantially on the input data. These data are continuously changing, both due to environmental changes (e.g., precipitation and temperature regimes, land cover and land use, forest parameters) and through the availability of new data sources and analytical methods. The goal of ALaDyn is to systematically account for these ongoing changes to ensure that risk assessments remain current and planning decisions can be made on a reliable basis.
Leveraging the benefits of long term land use data from HabitAlp with new remote sensing data and methods
Objective HabitAlp2.0 was a third-party funded project aiming to assess the natural landscape characteristics of national parks and large protected areas in the Alps using remote sensing methods (initially based on stereo aerial image analysis).
Project duration: 01.10.2024 – 31.12.2025
Funding: Austrian Research Promotion Agency (FFG)
Funding: € 71.020,--
Staff members: Manuela Hirschmugl (project lead), Harald Kristen
Cooperation partners: JOANNEUM RESEARCH Forschungsgesellschaft mbH (AT), Nationalpark Gesäuse GmbH (AT)
Project description
HabitAlp2.0 was a third-party funded project aiming to assess the natural landscape characteristics of national parks and large protected areas in the Alps using remote sensing methods (initially based on stereo aerial image analysis). Repeated acquisitions provide insights into dynamic landscape changes, which are largely driven by natural processes (e.g. rockfall flooding debris flows, avalanches, snow pressure wind influence, and natural fires) as well as site-related changes induced by climate change.
However, repeating the HabitAlp methodology developed around 20 years ago is highly time-consuming and therefore costly. This study therefore developed new approaches to enable a faster and more cost-efficient detection of these change processes. The methodological advancement focused on using the geometries of existing HabitAlp datasets to develop a computer-based classification model based on historical and recent remote sensing data (aerial imagery, satellite imagery, Lidar data, etc.).
The existing HabitAlp datasets served as a reference dataset and provided the basis for re-mapping. By using temporally high-resolution satellite imagery and, if available, Lidar data, both changes in the spatial extent of habitat types and qualitative changes across large areas could be mapped in a timely manner.
Boosting EU Biodiversity STrategy by empowering high education curricula and green skills for NATURE protection and restoration
Objective
BestNature is a cooperative European education project with the aim of improving the education of students in the field of biodiversity monitoring and protected areas.
Project duration: 2023-2026
Funding body: European Union (ERASMUS+)
Funding: € 71.043,--
Staff members:Manuela Hirschmugl (project manager), Harald Zandler
Cooperation partners: University of Tuscia (IT), University of Bologna (IT), Carabinieri Forestali (Biodiversity Group) (IT), University of Passau (DE), Carinthia University of Applied Sciences (AT), Institute of Ecology - E.C.O. (AT)
Project description
BestNature is a cooperative European educational project (ERASMUS+) with the aim of improving the education of students at all levels (Bachelor, Master, PhD) in the field of biodiversity and protected area monitoring. Interdisciplinary, cross-national and cross-university course modules are developed and applied together with the partners. Feedback from the students during the course of the program is used for continuous improvement. Three fieldwork weeks in the partner countries (Italy, Austria and Germany), during which researchers teach and learn together with students in protected areas, round off the project.
Objective
Graz has been researching the urban climate for decades. The KIS is now being developed from the previous urban climate analysis and extended to the city region. An interdisciplinary team from various fields such as climatology, spatial planning, remote sensing, urban water management and the environment is working together in the KIS.
Project duration: 2020-2025
Funding body: City of Graz / Province of Styria
Funding: € 125.000,--
Employees:Wolfgang Sulzer (project manager), Reinhold Lazar, Thomas Posch, Nina Polous, Benjamin Signitzer, Selina Schaar
Cooperation partners: Graz University of Technology, University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences Vienna, Geosphere Austria, (IT), Surveying AVT-ZT Imst, Joanneum Research, HTflux Engineering GmbH, and others
Project description
The long-standing collaboration between the City of Graz and the Institute of Geography and Spatial Research at the Karl-Franzens University has resulted in a comprehensive analysis of the urban climate from 1986, 1996, 2004 and 2011. The findings of the urban climate analyses - in particular with the climate top map and the map of planning information - were taken into account in various planning instruments such as the urban development concept or the zoning plan.
As part of the development of the Graz Climate Information System (KIS Graz), another thermal scanner flight was carried out in summer 2021. For the first time, the Graz city area and parts of the Styrian central region were flown together. The area to be flown covered an area of around 600 km² and extends from Deutschfeistritz in the north to Wildon in the south, Vasoldsberg in the east and Tobelbad and Premmstätten in the west.
The following work packages are being implemented:
-
Accompanying measurement campaigns for the thermal scanner flights
-
Urban climatological analysis of the aerial surveys (creation of surface temperature maps)
-
Creation of a climate analysis map and a planning information map
-
Evaluation of the (climate) modeling for the time of the thermal flights in 2021
-
Adaptation/updating and preparation of climate (element) maps
-
Cartographic preparation of the GIS data sets
Selected publications
- Sulzer, Wolfgang; Hirländer, Daniela, 2022: A remote sensing-based analysis of the thermal behavior of Gründerzeit courtyards in Graz. In: GEOGRAZ. Grazer Mitteilungen der Geographie und Raumforschung. 71. 2022. 4-10
- Hirländer, D. and W. Sulzer, 2019: Analysis of airborne thermal images in relation to different urban structures and landuses in Graz. In: M. Kalivodová, I. Laco, A.Raniak (eds.): The 18th International Symposium on Problems of Landscape Ecological Research, diversity and biodiversity - Abstract Book. Bratislava. Institute of Landscape Ecology, Slovak Academy of Sciences, Bratislava, Slovak Republic. 2019. P. 43.
- Bauer, Ch., Kern, K.,; Sulzer, W., 2019: Detecting Hot Spots on high resolution airborne thermal imagery - an automatic process to improve roof heat loss detection. In: Austrian Geographical Society. Mitteilungen. pp. 271-290. Vienna 2019, doi.org/10.1553/moegg161s271. In: Communications of the Austrian Geographical Society. 161. 2019. 271-290. doi:10.1553/moegg161s271
- Sulzer, W., 2018: Remote sensing based approach for monitoring urban growth in Graz / Austria. In: Grazer Schriften der Geographie und Raumforschung, Vol. (2018), H. 48: Spatial Tensions - Future Chances (2nd ed.), 111-120.
- W. Sulzer, K. Kern, Chr. Bauer, R. Lazar, M. Mudri, W. Ganster, 2016: Remote sensing-based heat loss detection of roof surfaces as a contribution to increasing the energy efficiency of urban spaces - results of a case study in Graz/Austria. In: M. SCHRENK, V.V. POPOVICH, P.ZEILE, P.ELISEI, C. BEYER (ed.): REAL CORP 2016 Proceedings/Tagungsband, June 22-24, 2016; 13S.
- Lazar, R. and W. Sulzer, 2013: Urban climate analyses Graz 1986 - 1996 - 2004 - 2011. Municipality of Graz, 297p. https://www.graz.at/cms/dokumente/10282564_11988940/afb7face/131128_StadtklimaTeil1.pdf https://www.graz.at/cms/dokumente/10282564_11988940/0096d0d3/131128_StadtklimaTeil2.pdf https://www.graz.at/cms/dokumente/10282564_11988940/ec6d9561/131128_StadtklimaTeil3.pdf
Objective
RestorEO aims to develop a quantitative, transparent and reliable monitoring system that provides information on the biodiversity status of ecosystems and is capable of relieving the responsible public authorities of their monitoring obligations. To this end, existing field work will be combined with Copernicus and other remote sensing data to quantitatively assess the degradation and restoration status of three important ecosystems: grasslands, forests and wetlands.
Project duration: 2022-2024
Funding body: Austrian Space Application Program (ASAP)- FFG
Funding: € 88.107,--
Employees:Manuela Hirschmugl (project manager), Florian Lippl
Cooperation partners: Joanneum Research Forschungsgesellschaft mbH, Institute for Ecology (E.C.O.) and the Federal Environment Agency
Project description
The loss of biodiversity, on which we all depend, is progressing faster than ever. In the context of the European Green Deal and the UN Convention on Biological Diversity, the EU Biodiversity Strategy 2030 announced the creation of an EU-wide plan to restore nature as one of its central contents. As part of this plan, the European Commission formulated legally binding targets for the restoration of nature in June 2022. The aim is to put Europe's biodiversity on the road to recovery by 2030 and beyond. In future, the countries must therefore also report accordingly on the measures, implementation and achievement of these legally binding targets. These reports require a quantitative and transparent, legally recognized monitoring system that provides reliable information on the status of biodiversity and is capable of relieving the responsible public authorities of their monitoring obligations. Such a monitoring system does not yet exist. Existing Austria-wide monitoring projects (e.g. FFH Art. 11 monitoring, biodiversity monitoring) are currently carried out on the basis of random samples. Such statistical approaches are precise enough on a large scale (e.g. for the whole of Austria) to be able to make policy-relevant statements. However, they are not useful for evaluating local restoration projects because it is very unlikely that a sufficient sample of these projects (or any of these projects at all) will be included in the nationwide monitoring sample. Furthermore, such field sampling is costly and time-consuming, which stands in the way of frequent updating and thus the provision of timely information. RestorEO will close this gap by combining the existing field work with Copernicus and other remote sensing data to develop an area-wide and quantitative monitoring of the degradation status or integrity of important ecosystems. Ecosystems were selected for development and piloting based on the following criteria: 1) the ecosystem and landscape degradation status assessment and priorities identified in the final report "Strategic Framework for Ecosystem Restoration" [Paternoster et al., 2021]; 2) the potential of Copernicus and other remote sensing data for monitoring these ecosystems; and 3) the carbon sequestration potential of these ecosystems. This selection process is also based on the European Commission's priorities for the restoration of degraded ecosystems. From these criteria, three ecosystems were derived that will be addressed in RestorEO: Forest, Wetlands and Grassland-dominated Cultivated Landscapes. For the forest ecosystem, the existing parameters for assessing condition are to be further developed on the basis of average values per district forestry inspection to provide an area-specific representation (tree species composition, fragmentation). In addition, further parameters important for the assessment of biodiversity, such as vertical structure or crown dimensions, will be derived. For the monitoring of grassland-dominated cultivated landscapes, these are the number of mowing times and the classification of meadow types, which can be derived from Sentinel-1 and -2 time series and used for the development of indicators. For wetlands, the spatio-temporal change in hydrology and vegetation structure and the observation of indicator species play a central role in the development of the monitoring system. For all ecosystems, it is important to map changes in vegetation and land use in a spatially explicit manner and as close to real time as possible. The overall aim is to support public administration at all levels with reliable data and information when preparing reports. The spatially differentiated results also enable local stakeholders such as national park managers, nature conservation authorities etc. to benefit from the results, as targeted local measures can be initiated on the basis of the area-based information provided by the monitoring system.
Publications
- Miletich, Petra; Kirchmair, Marco; Deutscher, Janik Gregory; Schippl, Alexander; Hirschmugl, Manuela: Open and Free Sentinel-2 Mowing Event Data for Austria. In: Remote Sensing. 17,10. 2025. 1-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101769
- Hirschmugl, Manuela and Lippl, Florian and Miletich, Petra and Hecke, Corinna and Posch, Larissa and Kirchmeir, Hanns: Remote sensing for monitoring restoration efforts in Alpine areas. In: Nared, J., I. Potočnik Slavič, Ž. Novljan, E. Frank, V. Braun (Hg.): Conference Booklet: The Alps - a Refuge of Bio- and Geodiversity? Ljubljana. ISCAR. 2024. 54.
- Fernerkundungsbasiertes Monitoring von Biodiversität und Ökosystemrestaurierung. In: Verein für Ökologie und Umweltforschung (Hg.): Maßnahmen & Monitoring: Rücksicht auf Natur und Biodiversität bei der Energiewende. Wien. facultas. 2024. 87 - 95.
Accompanying scientific research on the development of the Graz-Reininghaus and Waagner Biro districts (Smart City Graz) based on a climatological measurement campaign
Project duration: 2019-2024
Project team members: Wolfgang Sulzer (project manager at the IGR), Reinhold Lazar
Project partner: Borovsky & Duschek GmbH / engineering office for geography
Funding body: City of Graz
Project description
The City of Graz is planning to create its own urban climatological model. In this respect, the data basis is to be supplemented by climate monitoring of the district development in Graz-Reininghaus and Waagner Biro (Smart City Graz). A flexible measurement campaign is to be carried out in these two districts for a period of 5 years using measurement hardware provided by the City of Graz and a number of additional stations to be determined for a close-meshed measurement network. In addition, temperature measurement trips are to be carried out with mobile measuring devices and a thermal imaging infrared camera for detailed spatial determination of the temperature conditions.
Merging and harmonizing the data from the LTER sites "NP Gesäuse" and "Johnsbachtal" to establish the joint site "Gesäuse - Johnsbach"
Objective
The aim of the project is to compile and harmonize relevant data from the Gesäuse National Park and the Johnsbach Valley for the European Long-Term Ecosystem Monitoring (eLTER) in order to make them freely accessible in a central database (DEIMS).
Project duration: 2023 - 2024
Funding: € 28.100,--
Funding body: Austrian Academy of Sciences (ÖAW)
Staff members: Manuela Hirschmugl (project leader), Wolfgang Schöner, Florian Lippl
Cooperation partners: Wegener Center for Climate and Global Change; Gesäuse National Park
Project description
Current situation: For long-term monitoring, selected observations, so-called standard observations (SO), are to be recorded for all ecosystem areas (atmosphere, social and economic sphere, biosphere, hydrosphere and geosphere) using the so-called WAILS approach (Whole system Approach for In-situ research on Life Supporting systems). These are currently collected separately for the National Park and for the Johnsbach Valley, and not all of them are collected in a standardized form and/or not completely. Meteorological and hydrological parameters for both regions are provided by WegenerNet.
In the area of the biosphere, only a few parameters are currently integrated into the Dynamic Ecological Information Management System (DEIMS, DEIMS-SDR | Site and Dataset Registry). Access to socio-economic information (e.g. income, population, etc.) is generally available via Statistics Austria and the European Environment Agency. However, this data is not yet offered in accordance with eLTER standards. There are still few observations in the geosphere, although efforts are currently being made to derive soil parameters.
Objective: Based on all these existing observations, this project will evaluate their contribution to the eLTER Standard Observations. All available data will be collected, processed accordingly and integrated with standardized metadata into the DEIMS and additionally into a separate data paper. Furthermore, additional SOs will be derived from remote sensing data and an analysis of the deficits will be carried out.
Publications
- Lippl, Florian; Maringer, Alexander; Kurka, Margit; Abermann, Jakob; Schöner, Wolfgang; Hirschmugl, Manuela: A Benchmark Data Set for Long-Term Monitoring in the eLTER Site Gesäuse-Johnsbachtal.In: Data. 9(5),72. 2024. 13p. doi.org10.3390/data9050072
Recording of private swimming pools in Graz and Styria using remote sensing
- Project duration: 2016-2022
- Funding: City of Graz and Province of Styria
- Employees: Wolfgang Sulzer (project manager), Ariane Droin, Matthias Wecht, Philipp Gindl
Project description
Orthophotos from the City of Graz and the Province of Styria are available as a basis for mapping private swimming pools. In the first phase of the project, the pools are mapped predominantly analog/visually using heterogeneous data sources ranging from panchromatic orthophotos to multispectral UltraCam data. For those data bases that have an infrared channel, water indices were also calculated, which made it easier to identify open water areas and also to differentiate between trampolines. This made it possible to create a swimming pool cadastre for Graz for the period 1945 to 2018. The data is updated after each aerial survey.
In the second phase of the project, a survey of swimming pools is now to be carried out for the entire province of Styria. Deep learning algorithms will be used to map the digital orthophotos.
Selected publications
- Sulzer, W., Droin, A. and M. Wecht, 2016: The generation of a swimming pool cadastre for Graz (1945 - 2015). In: Revija za Geografijo. 22,11-2. 2016. 71-80. http://www.ff.um.si/zalozba-in-knjigarna/ponudba/zbirke-in-revije/revija-za-geografijo/clanki/stevilka-11-2-2016/rg2211-206droin,sulzer,wecht-thegenerationofaswimmingpoolcadastreforgraz(1945%E2%80%932015).pdf
Exploration of the Mutual benefits from Joint Use of GEDI and Sentinel-1 / Sentinel-2 data
The aim of this project is to combine satellite-based LiDAR data (GEDI) with Sentinel-1 and -2 for the area-wide derivation of vegetation parameters for forest monitoring.
- Project duration: 2021-2022
- Funding: Austrian Space Application Program (ASAP) 17 - FFG
- Staff members: Manuela Hirschmugl (project leader), Florian Lippl, Hannah Scheicher
- Cooperation partners: Joanneum Research Forschungsgesellschaft mbH
Project description
GEDI stands for "Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation" and is a geodetic laser scanner system on board the International Space Station (ISS). It provides point-by-point high-resolution backscatter curves of 3D structures on Earth, from which information on vegetation heights, vertical structure and distribution within the vegetation as well as biomass can be generated. In this project, the combination of GEDI with Sentinel-1 (S-1) and -2 (S-2) data is investigated, from which, in contrast to GEDI data, areal information can be derived. The aim of the present project is to evaluate the synergetic benefits of the three sensor types: LiDAR, optical and SAR and to explore the practical application in European and tropical forests.
Publications
- Hirschmugl, Manuela und Lippl, Florian und Sobe, Carina: Assessing the Vertical Structure of Forests Using Airborne and Spaceborne LiDAR Data in the Austrian Alps. In: Remote Sensing. 15,3. 2023. 664. http://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030664
Scientific analysis of the question of rural exodus (especially) of younger women from the region of south-eastern Styria - based on data from our own and external surveys. Development of solution strategies
- Project duration: 2019-2021
- Funding: LEADER/Office of the Styrian Provincial Government
- Employees: Josef Gspurning (management; together with student assistants)
- Cooperation partners:
- Regional Management Südoststeiermark
- Styrian Volcano Region GmbH
- Schools in the region
-
Further links: https://www.vulkanland.at/lebenskultur/plattform-frauen-kraft-suedoststeiermark/das-projekt-frauen-kraft/
Project description
According to ÖROK, a population decline of 4.7% is forecast for south-eastern Styria by 2040. This decline can be attributed not only to demographic change and declining birth rates, but also to migration to urbanized areas, which young women in particular are considering. The reasons are often a higher density of adequate jobs, diverse educational opportunities and better infrastructure (child and elderly care, public transport, leisure facilities, etc.) in urban areas. However, it is not only the so-called "hard" location factors that are decisive, but also "soft" factors such as quality of life, social and cultural offerings and gender roles. In rural regions in particular, there is still some catching up to do in terms of equal participation of men and women in socially important tasks such as gainful employment, household, educational and care work as well as politics and voluntary work. The "Frauen.Kraft" project aims to identify challenges for women's lives in south-eastern Styria, but also to highlight opportunities by making women's diverse lifestyles visible.
The aim of this project is to impart knowledge about the "Lippizanerheimat" region across generations based on the principles of gamification.
- Project duration: 2017-2020
- Funding: LEADER/Office of the Styrian Provincial Government
- Employees: Josef Gspurning (project manager), Kerstin Dohr, Markus Pichler
- Cooperation partners:
- LAG Lippizanerheimat
- Interest groups and numerous schools from the region
-
Further links: https://www.zukunftsraumland.at/projekte/2732;
Project description
The project is based on the idea of bringing the Lipizzanerheimat region closer to visitors - and also interested locals - in the form of a parlor game and, like a travel guide, providing them with interesting facts, suggestions for leisure activities and further information, for example on the interrelationships within the region. The following thematic levels can be identified as part of the game development process: Firstly, the area of nature and its products (whether aesthetic in the sense of valuable landscape/natural monuments of - more "comprehensible" in the form of their products); the same applies to the area of culture, which covers the entire span between cultural objects (such as architectural monuments) and cultural "happenings". The game reflects the existing tourism offerings from hiking to sporting activities, cultural monuments and cultural facilities to health and wellness tourism.
Project duration: ongoing
Funding: ÖAV
Employees: Harald Zandler, Wolfgang Sulzer (Former: Gernot Seier)
Cooperation partners: Cascade University Graz, ÖAV, BOKU Vienna, Geosphere Austria, Hohe Tauern National Park
Project description
For over 100 years, Austria's glaciers have been surveyed by the ÖAV in order to document the associated changes. Due to rapid melting and rapid changes, it has become difficult to record changes using conventional terrestrial methods in many places in recent decades. The aim of this project is therefore to accurately map and document glacier changes using unmanned aerial vehicles with centimeter-precise RTK technology.
Selected publications
- Avian, M., Bauer, C., Schlogl, M., Widhalm, B., Gutjahr, KH., Paster, M., Hauer, C., Friessenbichler, M., Neureiter, A., Weyss, G., Flodl, P., Seier, G., Sulzer, W., 2020 The Status of Earth Observation Techniques in Monitoring High Mountain Environments at the Example of Pasterze Glacier, Austria: Data, Methods, Accuracies, Processes, and Scales. Remote Sensing 12(8), doi.org/10.3390/rs12081251
- Seier G., Kellerer-Pirklbauer A., Wecht M., Hirschmann S., Kaufmann V., Lieb G.K., Sulzer W., 2017. UAS-Based Change Detection of the Glacial and Proglacial Transition Zone at Pasterze Glacier, Austria. Remote Sensing. 9(6): Article 549. doi:10.3390/rs9060549
Project duration: ongoing
Funding: none
Employees: Harald Zandler, Wolfgang Sulzer (Former: Gernot Seier, Matthias Wecht)
Cooperation partners: Cascade Uni Graz, TU-Graz, Hohe Tauern National Park
Project description
Active rock glaciers are periglacial structures in the permafrost area of mountains. In order to analyze their movement patterns, measurements with high spatial resolution are required. In addition to terrestrial measurements, unmanned aerial vehicles with centimeter-precise RTK technology are an ideal tool for creating spatial models in various dimensions and recording changes over long periods of time. The aim of the project is therefore to use a long-term monitoring approach to create a database to answer a variety of research questions about rock glaciers and their changes in the Austrian Alps.
Selected publications
- Kaufmann V., Seier G., Sulzer W., Wecht M., Liu Q., Lauk G., Maurer M., 2018: Rock glacier monitoring using aerial photographs: conventional vs. UAV-based mapping - a comparative study. International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, The. XLII-1: 239-246. doi:10.5194/isprs-archives-XLII-1-239-2018
- Kaufmann V., Kellerer-Pirklbauer A., Seier G., 2021: Conventional and UAV-Based Aerial Surveys for Long-Term Monitoring (1954-2020) of a Highly Active Rock Glacier in Austria. Frontiers in Remote Sensing, 2, 732744. doi.org/10.3389/frsen.2021.732744
Change detection Algorithm with very high resolution UltraCam data
- Project duration: 2011-2019
- Funding: City of Graz
- Project team members: Wolfgang Sulzer (project leader), Katharina Kern, Marc Muick, Andreas Salentinig Florian Pfeiler, Michael Mollatz, Ariane Droin
Project description
The aim of this project is the development of a (semi-) automatic change detection algorithm and its application to the entire Graz city area. Special attention is paid to changes in the structure of buildings, sealing and vegetation. The data from the Ultracam aerial surveys from 2007/2011, 2011/2015 and 2015/2019 will be analyzed and compared. The algorithm is designed to perform change mapping in a single classification step in order to improve accuracy and minimize processing time and computational effort.
Selected publications
- Sulzer, W., Kern, K., Eichberger, S., 2009: Urban change extraction from aerial photographs and multispectral scanner - an applied study from Graz/Austria. In: D. Maktav (Ed.): Remote Sensing or a Changing Europe. Proceedings of the 28th Symposium of the European Association for Remote Sensing Laboratories, Istanbul, Turkey, June 2-5, 2008, IOP Press, 551-557
- Salentinig, A., 2012: Remote sensing change detection of urban environments with very high resolution Ultracam data, unpublished Masterthesis, Department of Geography and Regional Science, University of Graz
- Sulzer, W, and A. Salentinig, 2013: Change Detection Analysis Graz: 2007 - 2011. unpublished project report, Graz, 51 p.
- Sulzer, W. and Salentinig, A., 2014: Remote sensing change detection in urban environment of Graz/Austria with very high resolution UltraCam data. Editors: Manfred SCHRENK, Vasily V. POPOVICH, Peter ZEILE, Pietro ELISEI, Clemens BEYER: Proceedings/Tagungsband 12-14 September 2017 - www.corp.at ISBN 978-3-9504173-2-6 (CD), 978-3-9504173-3-3 (print), 87-98. https://programm.corp.at/cdrom2017/papers2017/CORP2017_11.pdf
- Sulzer, W.: Real mapping of urban development in Graz - Land use mapping 1945 - 2015. Magistrat Graz, 260p.
Object-oriented land cover classification of Graz (Austria) with special consideration of the third dimension
Project duration: 2012-2019
Funding: City of Graz
Project staff: Wolfgang Sulzer (project manager), Marc Muick, Ariane Droin, Christoph König
Project description
The project deals with the creation of land cover classifications from very high-resolution, digital ULTRACAM aerial image data from the years 2007, 2011, 2015, 2018 and 2019 for the urban area of Graz (Austria). The central part of the project work is the creation of the rule sets of the object-based classification and the handling of data-related problems such as the shaded image areas in the image data. The legend and the land cover classes were developed in cooperation with the Department of Green Space and Waters of the City of Graz and the Department of Photogrammetry of the Surveying Office of Graz. The aim here is to generate a planning basis for urban planning and urban development and for the Department for Green Spaces and Waters of the Graz City Administration. The regulations were developed and tested on the basis of test areas representing the different urban structures. Furthermore, the classifications were carried out using elevation models (LiDAR and photogrammetry). The aim of this work step was to develop a set of rules that was as representative as possible for the entire city of Graz. In a further step, the generated sets of rules were implemented for the entire city of Graz using the aerial image data from 2007 and subsequently evaluated. The possibility of grading the height of the vegetation in general and the forest class in particular, which was investigated in this work, enables, among other things, a new way of looking at the forest areas of the city of Graz. In particular, the representation of approximate individual tree segments makes this representation very realistic. This subject area was also depicted with separate individual maps as part of this work in order to increase interpretability. In the final part of the work, the overall set of rules was applied to the aerial image data from 2011 to 2019. The different recording dates (March, April, September and June) and the different geometric and radiometric resolution of the data posed new challenges for the classification. Finally, the overall project aimed to develop a generally valid evaluation methodology for future aerial survey projects of Stadtvermessung Graz in order to keep the evaluation effort (adaptation of the rules and regulations) as low as possible and to automate it.
Selected publications
- Sulzer, W., M. Muick, W. Ganster, 2013: Objektorientierte Landbedeckungsklassifikation von Graz (Österreich) unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der dritten Dimension. In: Manfred SCHRENK, Vasily V. POPOVICH, Peter ZEILE, Pietro ELISEI (Ed.), 2013: Proceedings REAL CORP 2013, 651-660.
- Muick, M., 2011: Objektorientierte Landbedeckungsklassifikation unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der dritten Dimension Am Beispiel dreier Testgebiete innerhalb der Stadt Graz. Unpublished. Master thesis at the Institute of Geography and Spatial Research, University of Graz, Graz, p.86, 2011.
- Sulzer, W., 2016: Real mapping of urban development in Graz - Land use mapping 1945 - 2015. Magistrat Graz, 260 p.
- Sulzer, W., 2018: Remote sensing based approach for monitoring urban growth in Graz / Austria. In: Grazer Schriften der Geographie und Raumforschung, Vol. (2018), H. 48: Spatial Tensions - Future Chances (2nd ed.), 111-120.
TIR4U - Thermal Infrared detection of Roof heat loss for University of Graz
- Project duration: 2013 (10 months)
- Funding: Province of Styria / City of Graz
- Employees: Dr. Wolfgang Sulzer (project manager), Katharina Kern, Dr. Christian Bauer, Dr. Reinhold Lazar, Martin Mudri
- Cooperation partners:
- Mudir Messtechnik (Martin Mudri)
- http://w ww.ibbd.at/
Project description
Due to the European and Austrian targets for the reduction of energy consumption and greenhouse gases, the thermal refurbishment and optimization of the energy efficiency of buildings is increasingly becoming the focus of media coverage. Measurements of temperature distributions on building facades using infrared thermography to visualize energy loss are already widely used. The use of airborne thermal sensors to record energy deficits on roof surfaces, on the other hand, is still a young field of research. New generations of high-resolution thermal sensors enable a more differentiated view of roof surfaces that emit a lot of heat. Comparable previous studies were mainly limited to a two-dimensional, qualitative investigation of uniform roof coverings. In this study, which examines buildings on the campus of the Karl-Franzens University of Graz, infrared remote sensing data is now being calibrated to different roof coverings for the first time. Finally, taking into account the conditions under the roof surface allows an analytical view of the upward heat flow. The inclusion of additional influencing factors serves to improve the methods and is combined in a separate work step to form a parameter catalog, which in turn is applied to selected buildings at the University of Graz as an example. The methods developed and the project results of the study will be made available to a broad public in the form of scientific and popular science publications, information events, geovisualization tools and newspaper reports in local daily and monthly journals. In addition, the topic is didactically prepared via the Styrian School Atlas and made available in an understandable form as an information offer for formal environmental education. The central contact and target group is also the public sector (such as Graz City Council and the Province of Styria), which is the owner of many public buildings in Graz and a sponsor of thermal renovations. The project thus positions itself as an awareness-raising measure in the context of climate-neutral action.
Selected publications
- Sulzer, W., Kern, K., Bauer, C., Salentinig, A., Lazar, R., Ganster, W., Lorber, G., Mudri, M., Legat, K., Mah, St. 2013: Visualization of "Urban Roof Heat Loss" in Graz. 14th Conference Proceedings 14th Climate Day - Climate Change, Impacts and Adaptation as well as Avoidance. Austrian Climate Day. Vienna, 2 pp.
- W. Sulzer, K. Kern, Chr. Bauer, R. Lazar, M. Mudri, W. Ganster, 2016: Remote sensing-based heat loss detection of roof surfaces as a contribution to increasing the energy efficiency of urban spaces - results of a case study in Graz/Austria. In: M. SCHRENK, V.V. POPOVICH, P.ZEILE, P.ELISEI, C. BEYER (ed.): REAL CORP 2016 Proceedings/Tagungsband, June 22-24, 2016; 13S. http://www.corp.at/archive/CORP2016_110.pdf
- Sulzer, W., Lazar, R., 2015: Climate effectiveness of green spaces in terms of sustainable settlement and development planning. Proceedings of the symposium on 1.12.2015, Stadtplanung Graz, 2-45.
- Sulzer, W. and Lazar, R., 2014: 40 years of urban climate analyses (1974-2014) for planning purposes in Graz/Austria. IGU Regional Conference, Kraków, Poland, August 18-22, 2014, 2014 Book of Abstracts, 1381.
A GIS-based digital information platform for people with visual impairments or blindness.
The aim of the project is to develop a webGIS-based tool to support the daily mobility of people with visual impairments or blindness. ASSIGNMENT C
- Project duration: 01-03-2015 to 31-03-2018 (3 years, 1 month)
- Project leader: Zimmermann-Janschitz Susanne
- Project staff: Drexel Sebastian, Dückelmann Antonia, Landauer Simon, Mandl Bettina, Obermeier Jana
- Project partners:
- Odilien-Verein zur Förderung Sehbehinderter und Blinder Steiermarks;
- SynerGIS Informationssysteme GmbH
- Funding: FFG (Austrian Research Promotion Agency)
- Further links:
- App: https://barrierefrei.uni-graz.at/ways2see/
- Project homepage (created by pupils with visual impairments from the Odilien School): http://www.ways2see.at
Project description
Mobility is the key to personal responsibility and independence. For people with visual impairments or blindness, movement in public spaces usually requires additional, individual orientation information that conventional navigation tools do not offer. In addition, the preparation of this information is crucial for the target group.
For this reason, comprehensive catalogs of content, orientation information and danger spots were developed - always together with the target group - in order to derive priorities and profiles for users. The application is based on a geographic information system whose algorithm for wayfinding is based on these profiles.
The internet application ways2see makes it possible to request individual directions with a variety of orientation information between a start and destination address. In addition, facilities in the immediate vicinity can be searched for and navigated to. Ways2see is characterized by a barrier-free design, the user interface of the application is suitable for screen readers, texts and maps are adapted to the target group. The application was implemented for the city of Graz.
Selected publications
- Zimmermann-Janschitz, Susanne (2022): Digital Media and Persons with Visual Impairment or Blindness. In: Paul C. Adams and Barney L. Warf (eds.): Routledge Handbook on Media Geographies. London and New York. Routledge. 2022. 74-91. doi:10.4324/9781003
- Zimmermann-Janschitz, Susanne; Landauer, Simon; Drexel, Sebastian; Obermeier, Jana (2021): Independent mobility for persons with VIB using GIS. In: Journal of Enabling Technologies. 15,3. 159.174. doi:10.1108/JET-03-2020-0
- Zimmermann-Janschitz, Susanne (2019): The Application of Geographic Information Systems to Support Wayfinding for People with Visual Impairments or Blindness. In: Giuseppe Lo Giudice (ed.): Visual Impairment and Blindness. London/Rieka. IntechOpen. 22. doi:10.5772/intechopen.89308
- Zimmermann-Janschitz, Susanne (2018): Geographic Information Systems in the context of disabilities. In: Journal of Accessibility and Design for All. 8,2. 161-193. doi:10.17411/jacces.v8i2.171
- Zimmermann-Janschitz, Susanne; Dückelmann, Antonia; Drexel, Sebastian; Obermeier, Jana; Landauer, Simon; (2018): Naturally SELF-DEPENDENT through the world. Kranzberg. ESRI Germany GesmbH.
- Zimmermann-Janschitz, Susanne; Mandl, Bettina; Dückelmann, Antonia (2017): Clustering the Mobility Needs of Persons with Visual Impairments or Legal Blindness. In: Transportation Research Record TRR. 2650. 2017. 66-73. doi:10.3141/2650-08